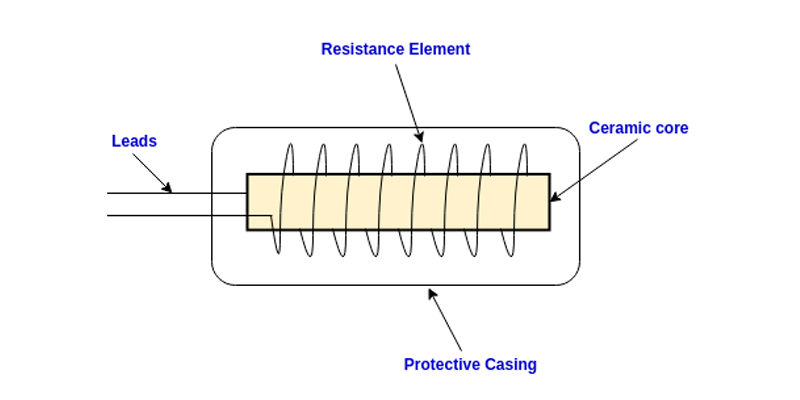
The resistance wire is coiled around a mica base to create the resistance temperature detector. To lessen the inductance effect, the wire is looped around the support like a helical coil. The leads (terminals) are pulled from the pipe. A stainless steel housing surrounds the coil to keep it safe. The graphic displays a wire coiled RTD’s structural aspect.
Resistance-Temperature-Detector-RTD-figure-diagram-construction
The most popular RTD materials are copper, nickel, and platinum. These metals are thermally insensitive and have positive temperature coefficients. Additionally, these materials’ resistance-temperature properties are essentially linear.
A thin layer of resistive material is deposited over a ceramic substance to create thin-film RTDs, another form of RTD.