Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) are precise temperature measuring instruments that are widely used in various industries due to their accuracy and reliability. This blog explores the uses and types of RTDs, providing insights into why they are a preferred choice for temperature measurement.
What are RTDs?
RTDs are temperature sensors that operate on the principle that the electrical resistance of certain materials changes predictably with temperature. Typically made from pure platinum, nickel, or copper, RTDs provide accurate and stable temperature readings.
Uses of RTDs
RTDs are versatile and can be found in numerous applications across different sectors. Here are some common uses:
- Industrial Applications:
- Process Control: In chemical and petrochemical industries, RTDs monitor and control process temperatures to ensure product quality and safety.
- Manufacturing: Used in plastic, textile, and food processing industries for precise temperature measurements during production.
- HVAC Systems:
- RTDs are integral in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to monitor and regulate indoor climate conditions.
- Power Generation:
- Essential in monitoring the temperature of generators, turbines, and other critical components to prevent overheating and ensure efficient operation.
- Automotive Industry:
- Employed in engine testing and monitoring, as well as in the development of battery systems for electric vehicles.
- Medical Equipment:
- Used in various medical devices, including incubators and sterilization equipment, due to their high accuracy and stability.
- Aerospace:
- Crucial in monitoring the temperature of aircraft engines and other components to ensure safety and performance.
- Laboratory Research:
- Utilized in scientific research for precise temperature measurements in experiments and data collection.
Types of RTDs
RTDs come in different types, each suited to specific applications and environments. Here are the primary types:
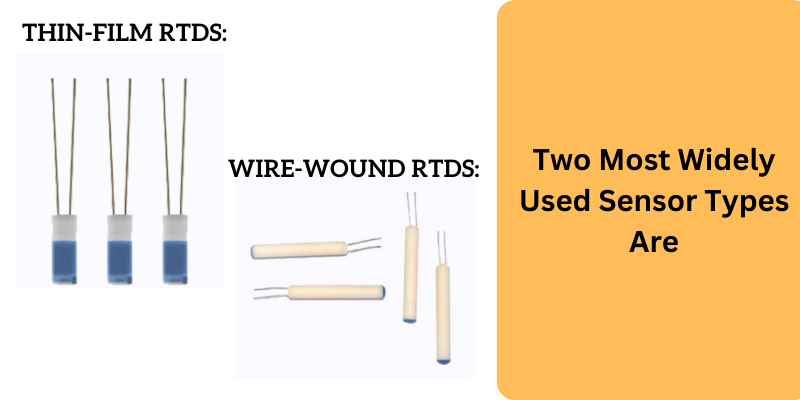
- Wire-Wound RTDs:
- Construction: Made by winding a thin wire of pure metal (usually platinum) around a ceramic or glass core.
- Advantages: Highly accurate and stable over a wide temperature range.
- Applications: Ideal for industrial and laboratory applications requiring high precision.
- Thin-Film RTDs:
- Construction: Consist of a thin layer of platinum deposited onto a ceramic substrate.
- Advantages: Smaller in size, faster response time, and cost-effective compared to wire-wound RTDs.
- Applications: Common in electronic devices, automotive sensors, and consumer electronics.
- Coiled RTDs:
- Construction: Feature a coil of platinum wire encased in a protective tube, allowing for expansion and contraction.
- Advantages: Flexible and can withstand mechanical shocks and vibrations.
- Applications: Suitable for harsh environments, such as power plants and heavy machinery.
- Film RTDs:
- Construction: Created by depositing a film of platinum onto a substrate.
- Advantages: Compact, robust, and can be integrated into electronic circuits.
- Applications: Used in applications requiring rapid temperature changes and small sensor sizes.
- Surface-Mount RTDs:
- Construction: Designed to be mounted directly onto a surface for temperature measurement.
- Advantages: Excellent for measuring surface temperatures and can be used in confined spaces.
- Applications: Common in semiconductor manufacturing, electronic devices, and surface temperature monitoring.
Conclusion
RTDs are indispensable tools in modern temperature measurement, offering precision, stability, and reliability. Their diverse applications range from industrial processes to medical devices, highlighting their versatility. Understanding the different types of RTDs and their specific advantages can help in selecting the right sensor for your application, ensuring accurate and efficient temperature monitoring.
For more information or to explore our range of RTD products, feel free to contact us or visit our website.












