When we talk about temperature measurement sensors, then RTD is the first sensor that comes in our mind.
RTD full form is a Resistance Temperature Detector.
RTD is used in many industrial applications, domestic applications, Household applications. RTD is the very basic sensor of temperature measurement.
In this blog, we are going to see the detailed information about RTD Sensor, What is RTD, RTD working principle, RTD meaning, etc.
What is RTD Sensor?
RTD defined by Wikipedia,
Resistance thermometers, also called Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs), are sensors used to measure temperature. Many RTD elements consist of a length of fine wire wrapped around a ceramic or glass core but other constructions are also used. The RTD wire is a pure material, typically platinum, nickel, or copper. The material has an accurate resistance/temperature relationship which is used to provide an indication of temperature
In simple words, I can say that RTD(Resistance Temperature Detectors) is a temperature sensor that changes its resistance according to temperature.
Construction of RTD Sensor
RTD is a device that resistance varies with the temperature. RTD is built with a resistive element or temperature sensing element, which contains either a coil of wire or thin-film with a sensing element attached in it.

Electrical resistance is measured from a distance away by attaching the copper cable with it. A protective sheath houses the sensing element. This element is usually Platinum because it has a wide range and linear relationship of resistance vs temperature.
| Temperature Range of Different Metals | |
| Metal | Temperature Range |
| Platinum | -200 °C to 850 °C |
| Nickle | -100 °C to 315 °C |
| Copper | -75 °C to 150 °C |
The types of material used to built the RTD will determine the temperature range of that RTD Sensor. Platinum is the most commonly used metal to build the RTD Sensor. Nickle and copper also used sometimes as a resistive element.
The below figure shows the temperature vs resistance graph of all three elements platinum, nickel and copper.

Working Principle of RTD Sensor
RTD Sensor works on this basic principle that as the temperature of the metal increases, resistance also increases. The value of resistance measured in ohms and equivalent temperature can be converted based on this resistance value.
The temperature coefficient of the RTD sensor is the average changes of resistance over the temperature range 0 °C to 100 °C and normally denoted by the α0
α0 = (R100 – R0)/(R0 x 100)
Where R100 = Resistance at 100 °C (ohm)
R0 = Resistance at 0 °C (ohm)
As per the above equation relationship between temperature and resistance may be expressed as,
Rt = R0 ( 1 + α0t)
Where Rt = Resistance of RTD sensor at temperature t °C (ohm)
R0 = Resistance at 0 °C (ohm)
α0 = Temperature co-efficient of RTD sensor at 0 °C
Examples of RTD Sensor
A PT100 RTD Sensor measures 100 Ω at 0 °C and 139.1 Ω at 100 °C. Calculate its temperature coefficient, Calculate the resistance at 40 °C and when the resistance is 116 Ω, find the temperature.
Calculate Temperature Coefficient
Temperature Coefficient (α0) = (R100 – R0)/(R0 x 100) = (139.1 – 100) / (100 x 100) = 0.00391 /°C
Calculate Resistance of RTD Sensor at 40 °C
Rt = R0 ( 1 + α0t) ⇒ R40 = 100 (1 + 0.00391 x 40) = 115.64 Ω
Calculate Temperature of RTD Sensor when the resistance is 116 Ω
Rt = R0 ( 1 + α0t) ⇒ 116 = 100 (1 + 0.00391 x t) ⇒ t = 0.16 / 0.00391 = 40.92 °C
Types of RTD
RTD is a passive element, by applying some voltage or using the Wheatstone bridge circuit we can detect the change in the resistance.
To measure this resistance value, the RTD sensor must be connected with the instrument using insulated copper wires. Like platinum, copper also has a resistance value. This lead wire resistance value of copper wire may impact the resistance value of the RTD sensor.
2-Wire RTD

2-Wire RTD is used where the approximate value of temperature is required. The cable lead resistance is also added which will cause an error in measurement.
3-Wire RTD
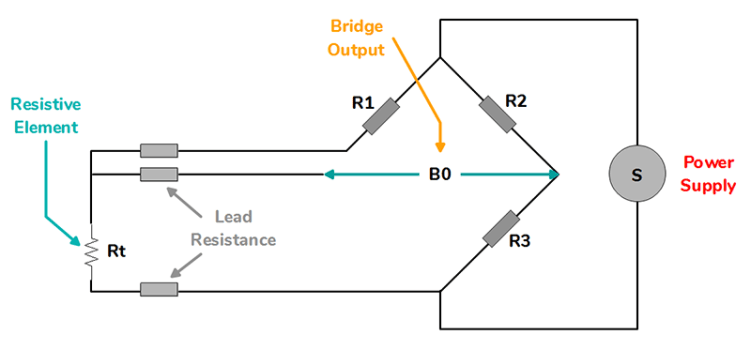
This type of RTD is widely used in industrial applications. There is a lead resistance in each arm which will cancel out the cable resistance as long as both leads are the same.
4-Wire RTD

Four-wire RTD configuration is the most accurate temperature measurement setup. When there is a high accuracy needed this type of RTD is used. This device measured and removed lead resistance in both sets of leads.
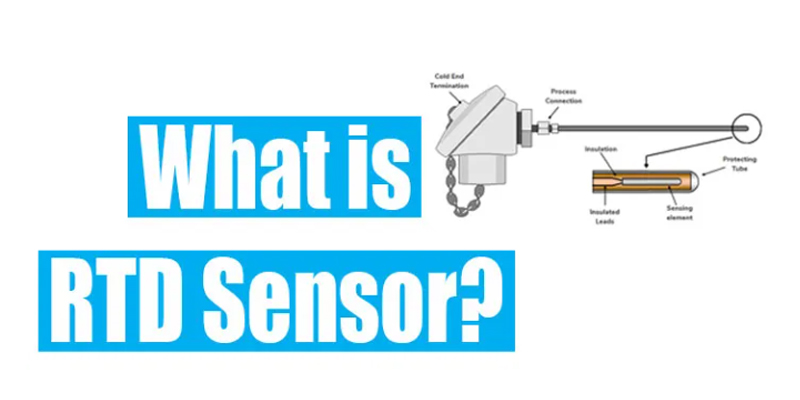
Components of RTD Sensor
Sensing Element
This is the actual temperature sensing metal element.
Protecting Tube
This tube protects the sensing element from the moisture and outside environment. This protecting tube is made mostly of stainless steel.
Process Connection
Process connection includes the standard fitting.
RTD Sensor Wire Configuration
RTD Sensor is available in 2-wire, 3-wire, and 4-wire configuration. The most commonly used configuration is a 3-wire RTD configuration and widely used in industrial applications.
Cold End Termination
RTD sensor can terminate with the controller like PLC, Closed-loop, PID, etc. through this cold end termination.
Steps to choose RTD Sensor
Some steps are considered while selecting the RTDs (Resistance thermometers, PT100, PT1000, etc)
Sensing Element Type
Which element is best suited for the application like PT100 or PT1000?
Application
RTD Sensor is being used to measure the temperature of liquid, gas or solid? Where is it going to fix like on the vessel, in the furnace, on a machine, etc?
Environment
What are the environmental conditions, where it is going to install? like IP rating, high vibration resistance, chemically protected, food use.
Location
How to RTD sensor is going to mount like wall-mounted, handheld, inside or outside, etc.
Operating Range
How much temperature is going to measure, like the range of temperature to measure by the RTD sensor?
Connection to Application
Where do you connect the feedback of the RTD sensor? What is the wiring configuration like 2-wire, 3-wire or 4-wire?
Advantage and Disadvantages of RTD Sensor
Advantages
- Good sensitivity
- Linear over a wide operating range
- Uses standard copper wire
- High temperature operating a range
- Copper RTD’s minimize the thermocouple effect
Disadvantages
- Bulky in size and fragile
- Self-heating problems
- More susceptible to electrical noise
- More expensive to test and diagnose
Summary
I hope you like this blog, you get all the details about RTD Sensor(usually known as PT100, Resistance Thermometer, Resistance Temperature Detector, etc.). This page gives you all the information about What does RTD stands for, Components, Application, Advantages, Disadvantages, Steps to choose, etc.
Source: InstrumentationBlog